

Electrolysis is widely used in the metallurgical industry, such as extracting metals from ore or compounds (electrolytic metallurgy) or purifying metals (electrolytic purification), and depositing metals from solutions (electroplating). Metal sodium and chlorine are produced by electrolysis and melting sodium chloride; electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride produces sodium hydroxide and chlorine. The electrolysis of water produces hydrogen and oxygen. The electrolysis of water is to decompose water into H2(g) and O2(g) under the action of an external electric field.
Electrolysis is a very powerful means to promote redox reactions. Many difficult redox reactions can be achieved by electrolysis. For example: the molten fluoride can be oxidized to elemental fluorine on the anode, and the molten lithium salt can be reduced to metallic lithium on the cathode. The electrolysis industry plays an important role in the national economy. Many non-ferrous metals (such as sodium, potassium, magnesium, aluminum, etc.) and rare metals (such as zirconium, hafnium, etc.) are smelted and metals (such as copper, zinc, lead, etc.) are refined. The preparation of basic chemical products (such as hydrogen, oxygen, caustic soda, potassium chlorate, hydrogen peroxide, oxonitrile, etc.), as well as electroplating, electropolishing, anodizing, etc., are all realized by electrolysis. "
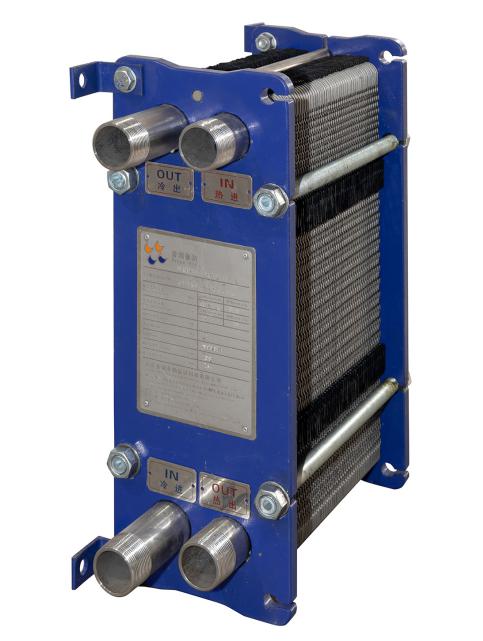
Heating and Cooling process for the Electrolyte. With Corrosion resistant plate heat exchanger.
Material of Plate: Hastelloy C276
Material of gasket: EPDM / FKM

TEL: 86-531-88683323
Email: sdpropellent@pl-heatexchanger.com
ADD: 5F, Xinsheng Building #2 Xinluo Street 1299, Hi-Tech District, Jinan, Shandong, China

 Español
Español